The role
of Claudin18.2
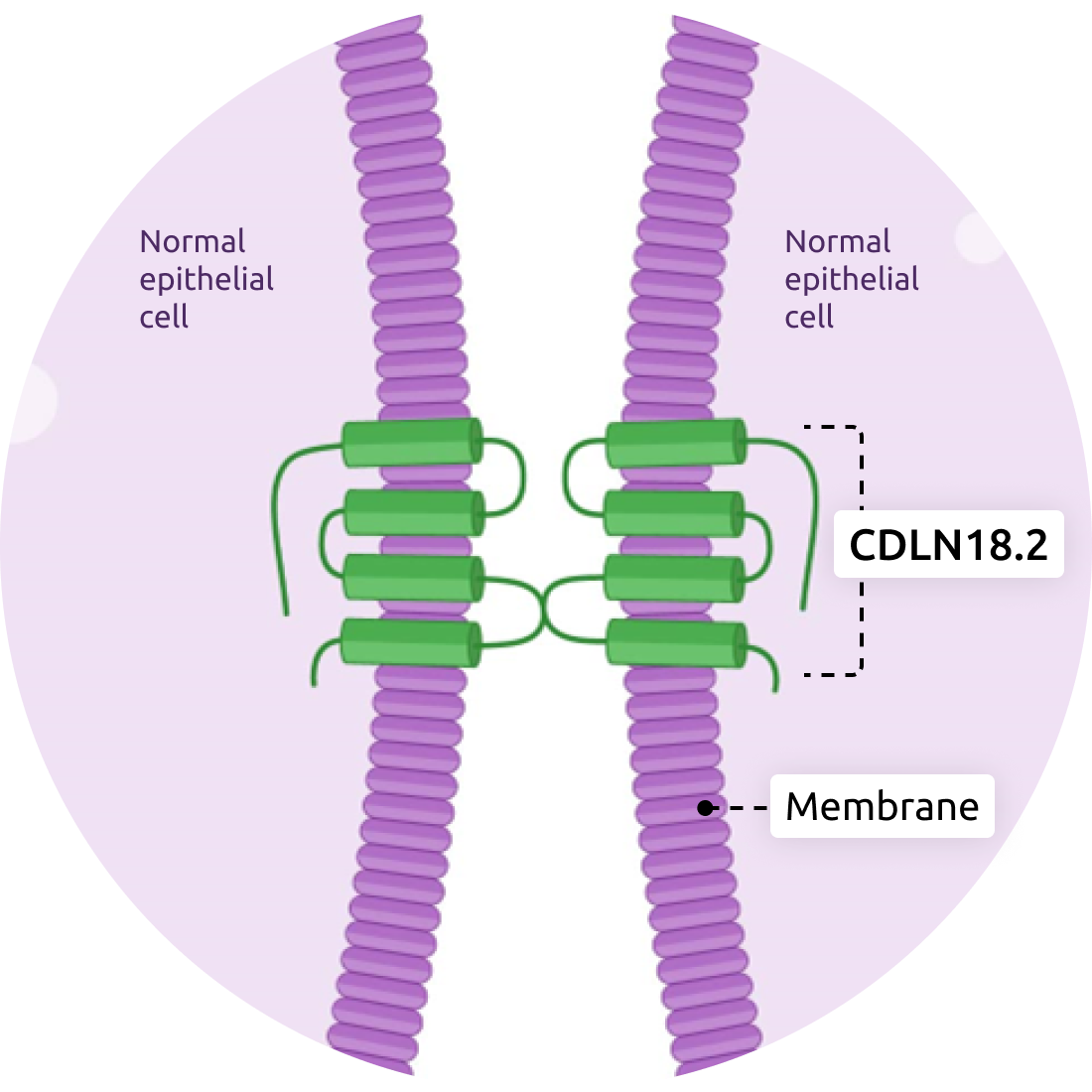
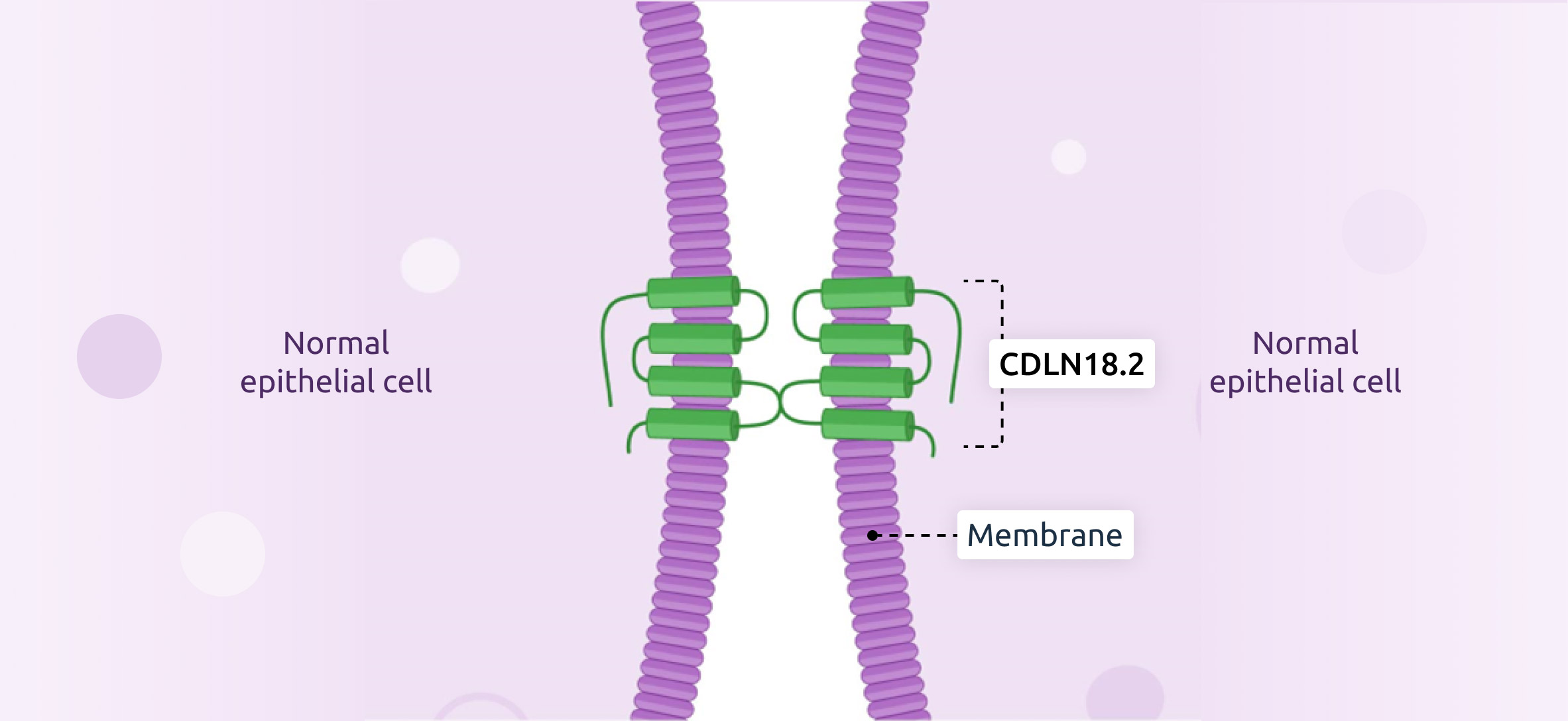
The cell surface molecule Claudin18.2 regulates barrier properties and contributes to cell-to-cell adhesion. It is a key component of the tight junction for cell polarity and sealing the spaces between adjacent cells. In normal tissue, expression of Claudin18.2 is very limited and largely inaccessible, as it is typically buried in the tight junction complex of gastric mucosal cells. In the development of cancer, however, cells lose their polarity and structure. As a result, Claudin18.2 may become exposed during tumorigenesis and accessible as a target for cancer therapy. Claudin18.2 is highly expressed on gastric cancer and pancreatic cancer cells and can also be present in esophageal, lung, and ovarian cancers. The expression pattern makes Claudin18.2 a highly selective biomarker for targeted cancer therapies.
Normal epithelial cells
- Regulates barrier properties and contributes to cell-to-cell adhesion.
- Expression very limited in normal tissue.
- Typically buried in the tight junction complex of gastric mucosal cells.
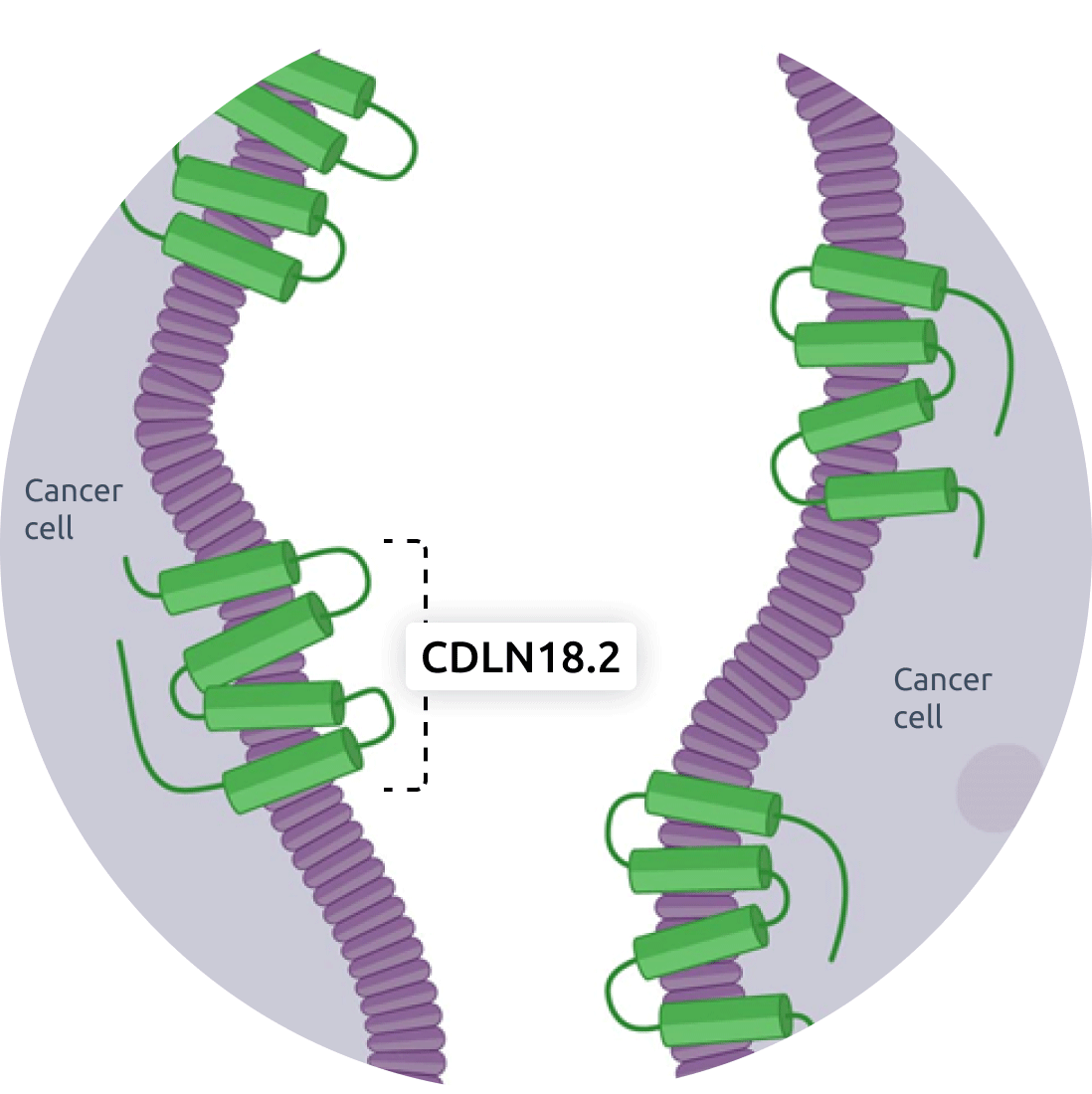
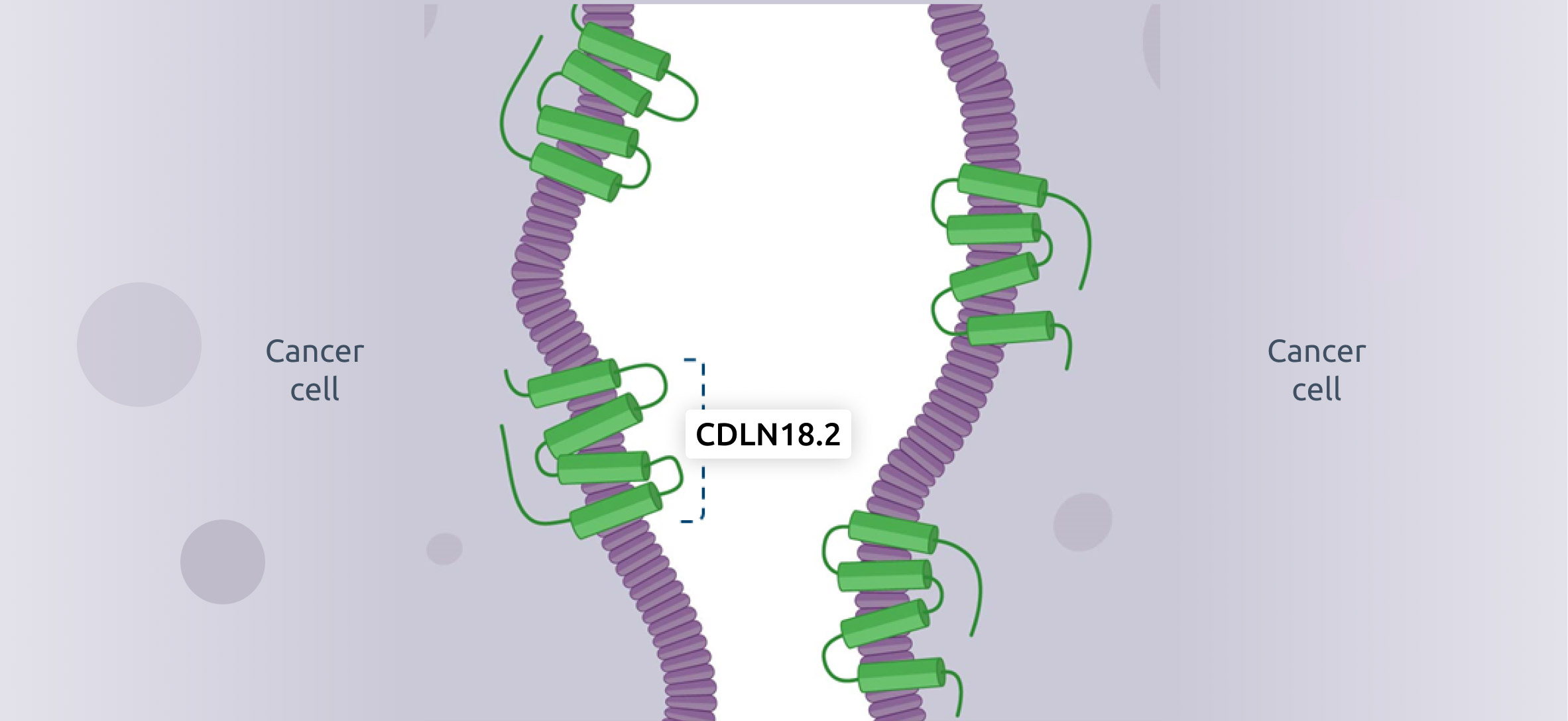
Cancer cells
- In cancer, cells lose their polarity and structure.
- CLDN18.2 is overexpressed in certain cancers including gastric cancer and pancreatic cancer.
- CLDN18.2 may be exposed and accessible as a target for cancer therapy.
Claudin18.2 is a validated target for cancer therapy, as randomized clinical trials with the chimeric anti-Claudin18.2 antibody zolbetuximab have shown a survival benefit in combination with chemotherapy in first-line gastric cancer patients whose tumors express high (75% or greater) and intense levels of Claudin18.2. However, since Claudin18.2 expression in tumors is heterogenous, expansion to patients with lower expression and improved efficacy in patients with higher expression would benefit from an antibody with higher affinity and improved killing activity.
VIEW OUR PROGRAM30-40%
gastric cancer patients have high (75%+) CLDN18.2 expression